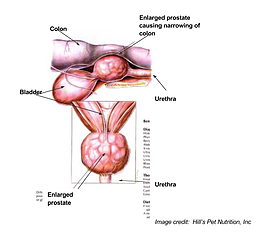
The prostate is a gland surrounding the urethra near the bladder in male dogs and cats. The purpose of the prostate gland is the production of sperm fluid. This gland can cause problems, especially in older, non-neutered pets. Prostate gland disease in neutered pets is uncommon. These problems include:
- Prostatitis – infection of the prostate
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) – enlargement of prostate due to hormonal imbalance
- Cancer
Symptoms of prostate disease:
- Pain in the area of the prostate
- Straining or pain when defecating sometimes resulting in constipation
- Straining or pain when urinating
- Blood in urine
- Discharge from the penis
Diagnosis of prostate disease depends on the individual, but may include:
- Urine culture and sensitivity to determine if and what bacteria may be infecting the prostate gland. This test helps determine which antibiotic will work best for treatment.
- Ultrasound – helps visualize the prostate. This test can also be used to guide a fine needle aspirate to collect a small sample of prostate tissue for analysis.
- Prostatic wash – this test allows analysis of the prostate fluid. Collection may require sedation or anesthesia.
Treatment depends on the cause of prostate gland disease but can include:
- Antibiotics
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Castration/neuter